Cardiovascular System: The Vascular System
1. Drag and drop the names of the five types of blood vessels to the correct place on the diagram below. You can restart the activity by using the blue button on the right. You will not be able to move labels around once placed.
Veins
Arterioles
Arteries
Capillaries
Venules
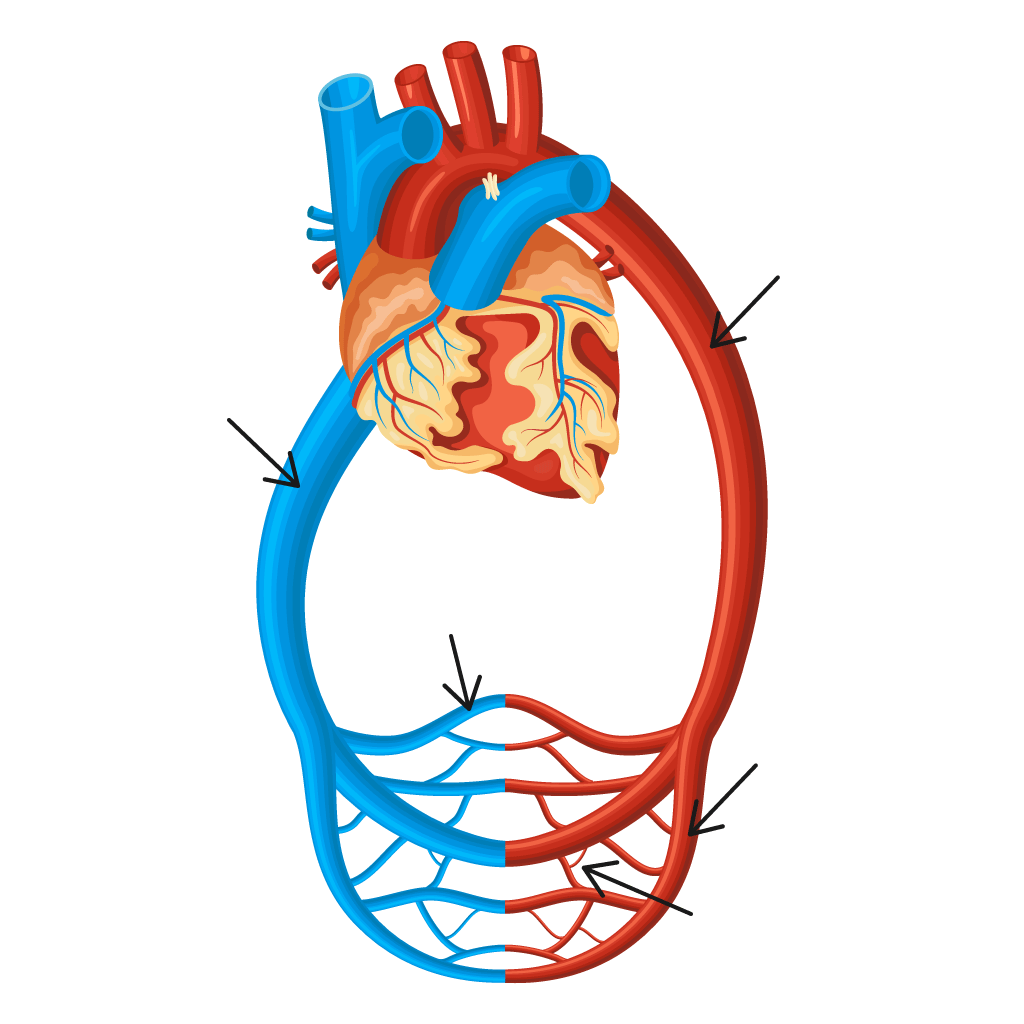
2. Connect the names of the different blood vessels to their descriptions.
Arteries
Veins
Capillaries
Arterioles
Venules
Smaller branches of arteries that can control distribution of blood through vasoconstriction and vasodilation.
Large muscular vessels that carry blood away from the heart.
Blood vessels that carry blood back to the heart at lower pressure. Contain valves to avoid backflow of blood.
Collect blood from the capillaries which then merge into larger vessels called Veins.
Tiny blood vessels with walls only one cell thick. Site for the exchange of gases and nutrients (Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide) between blood and tissue cells.
3. Explain how the distribution of blood to different parts of the body is influenced by blood vessels during exercise.
Type your answer in the box then check your answer against the model answer.
Arterioles contain a layer of smooth muscle which can contract and relax. When this contracts it limits blood flow meaning less blood flows through via a process known as Vasoconstriction. When the layer of muscle relaxes it allows more blood to flow through via a process known as Vasodilation. During exercise, blood is re-distributed to the working muscles from non-essential organs as the muscles require more oxygen. To enable this, arterioles leading to non-essential organs such as the liver and stomach vasoconstrict whereas arterioles leading to the working muscles vasodilate.
Cardiovascular System: Heart Structure
(1)
Cardiovascular System: Heart Function
(2)
Cardiovascular System: Functions of Cardiovascular System
(3)
Cardiovascular System: Blood Pressure
(4)
Cardiovascular System: The Vascular System
(5)
Respiratory System: Structure
(6)
Respiratory System: Function
(7)
Respiratory System: Breathing
(8)
Respiratory System: Lung Volumes
(9)
Introduction to short and long term effects of exercise
(10)
Short term cardiovascular responses to exercise
(11)
Short term respiratory responses to exercise
(12)
Short term muscular and skeletal responses to exercise
(13)
Introduction to long term adaptations to exercise
(14)
Long term cardiovascular adaptations to exercise
(15)
Long term respiratory adaptations to exercise
(16)
Long term muscular and skeletal adaptations to exercise
(17)